Image mode for Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Use container technologies to build, deploy and manage your operating system with the same tools and workflows as applications, promoting a common experience and language across teams.

What is image mode for Red Hat Enterprise Linux ?
Image mode for Red Hat® Enterprise Linux® (RHEL) is a simple, consistent approach to build, deploy and manage the operating system using container technologies. Now you can manage the operating system with the same tools and workflows as applications, promoting a common experience and language across teams.
Available in tech preview for RHEL 9, this new approach utilizes bootc and reduces complexity across the enterprise by letting development, operations, and solution providers use the same container-native tools and workflows. This includes GitOps and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD), to manage everything from applications to the underlying OS.
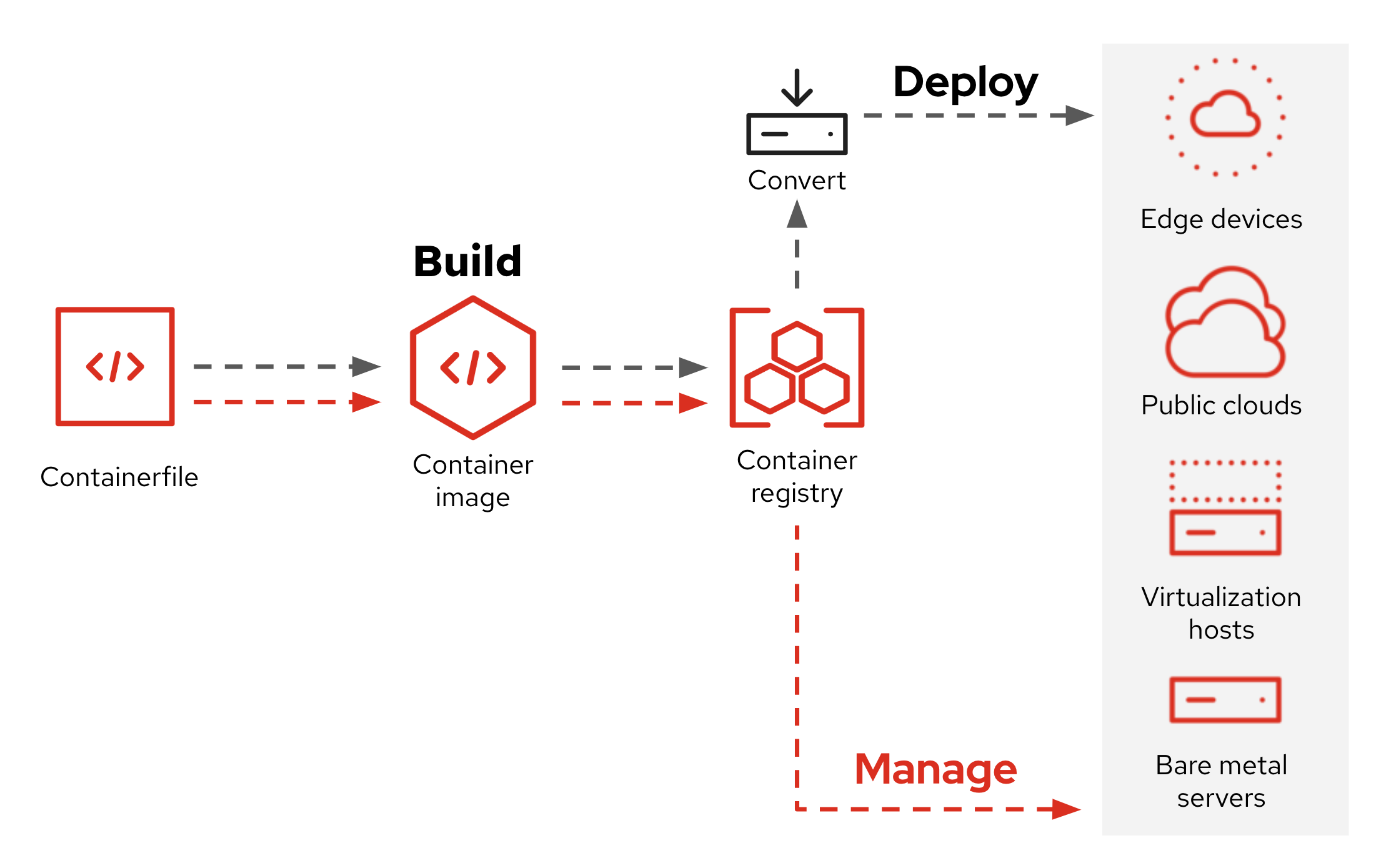
Users can leverage image mode to encapsulate runtimes, drivers, dependencies, and applications to bridge gaps between the operation teams and the application development cycle. Deployment is also straightforward - from the data center to public clouds - and can be used on bare-metal servers, virtual machines, and even edge devices.
How does image mode for RHEL use containers?
Bootc: Image mode leverages the bootc tool to build and deploy Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Bootc stands for bootable container, and the image will include the kernel, bootloader, and other items typically excluded from application containers. From there, you can add any software or dependency needed, build the image, and then push it to a registry. When complete, we’ll use image builder to convert to a disk image. We can deploy a vmdk, qcow2, an AMI, etc. These are quick to generate, and bare metal works great too.
Expanded functionality: The bootc tool also applies a container image as an update to manage an already running Linux system. The contents are written to the existing filesystem, switching out the /usr and /boot directories of the Linux system. By default, these systems automatically update themselves when a new version of their bootc image is tagged in the container registry.