In the previous article in this series, you learned how to deploy Java applications to Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform (JBoss EAP) using Helm on Red Hat OpenShift. Developers can use the procedures in Part 1 to easily stand up traditional Java application servers on Kubernetes with predefined Kubernetes manifestos.
What if you could have the same benefits when you develop microservices using JBoss EAP and Helm charts? JBoss EAP provides the Extension Pack (XP) to implement content trimming, packaging to a bootable JAR, and a MicroProfile specification including fault tolerance, monitoring, and tracing in support of microservices in the cloud. This article explains how to make a bootable JAR using JBoss EAP XP and Helm and deploy the application to OpenShift.
Build a bootable JAR with JBoss EAP XP and Helm
You will use the same Todo backend application that you deployed in the previous article. At the end of the tutorial, you will have both a traditional enterprise Java application and a bootable JAR for lightweight and independent deployment such as a microservices architecture, using a JBoss EAP XP Helm chart as shown in Figure 1.
Note: The Helm charts for JBoss EAP 7.4 are a technology preview feature on OpenShift 4.8, so support is limited when you use these features in production environments.

Installing a JBoss EAP XP Helm chart
Go to the developer console in Red Hat OpenShift and navigate to the Topology view. You will add the same project (eap-helm-demo) to OpenShift that you used in the previous article.
Click the Add to Project icon on the left side and enter EAP into the search box. Then select the Eap Xp3 v1.1.0 Helm chart and click Install Helm Chart, as shown in Figure 2.
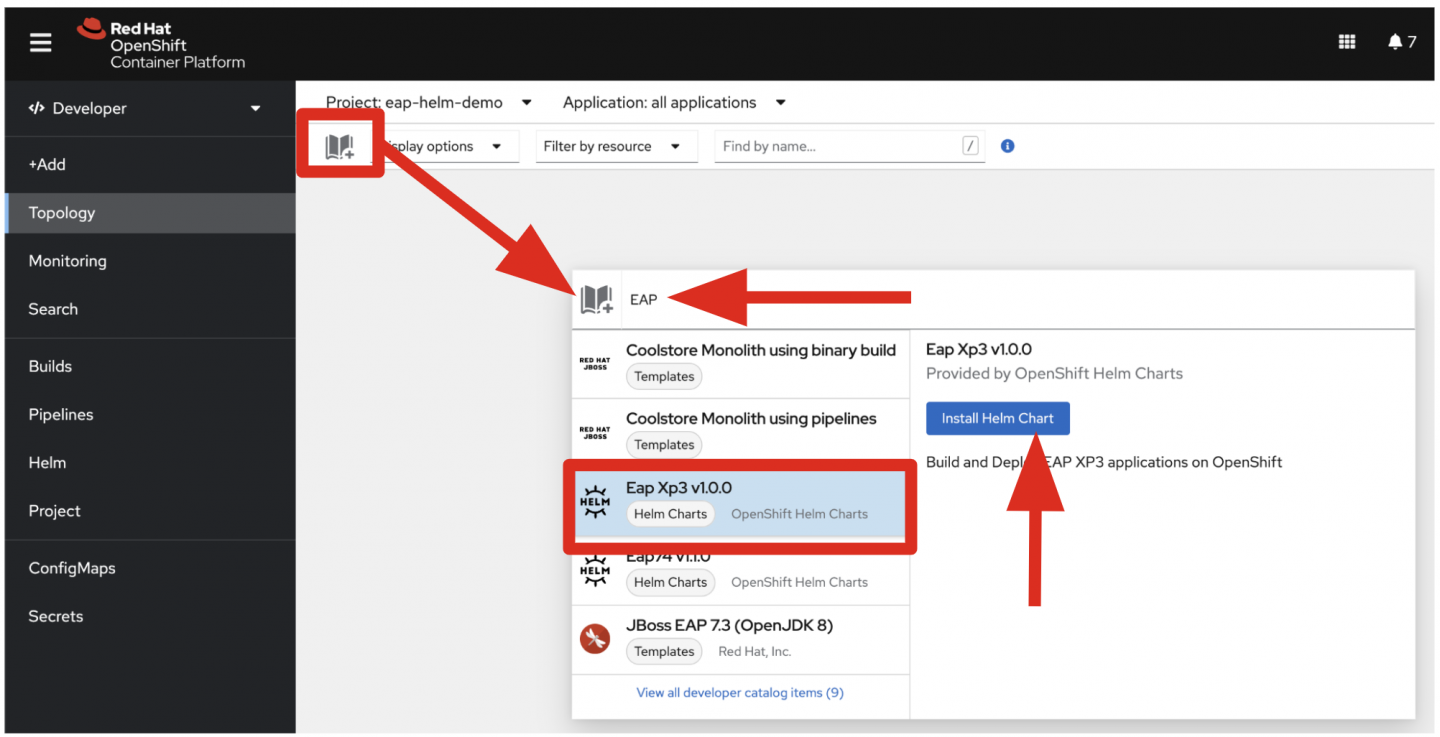
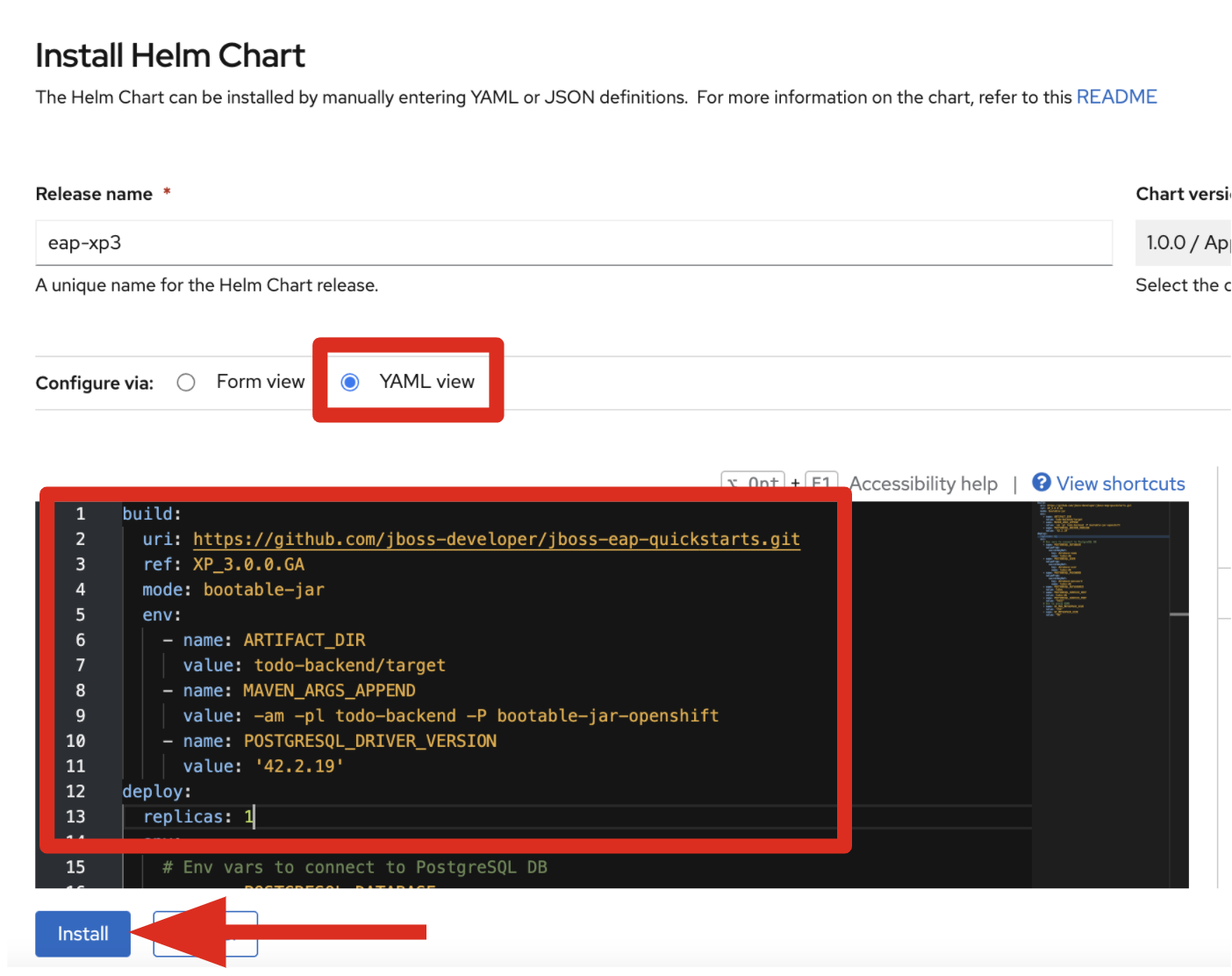
Now define a specific build, image, and deployment for a bootable Todo back-end application. Switch to the YAML view to add build and deploy configurations, as shown in Figure 3. Use bootable JAR mode with the environment variables required for your PostgreSQL data source in your build. Also, set a single runtime using the replicas field in the deploy property:
build:
mode: bootable-jar
env:
- name: MAVEN_ARGS_APPEND
value: -am -pl todo-backend -P bootable-jar-openshift
- name: POSTGRESQL_DRIVER_VERSION
value: '42.2.19'
deploy:
replicas: 1
After you add the custom configuration in the YAML configuration, click on the Install button. You can find the entire YAML configuration at the Todo back-end repository.
Note: You will probably see an ErrImagePull or ImagePullBackOff message in the resources, as shown in Figure 4. Don't worry—your bootable JAR is building successfully, but your deployment will report ErrImagePull and ImagePullBackOff until the build is complete.

Once the application build is complete, your image is automatically rolled out as shown in Figure 5. Create a connector between the JBoss EAP XP pod (Helm icon) and the PostgreSQL pod via the drag-and-drop feature in the Topology view.
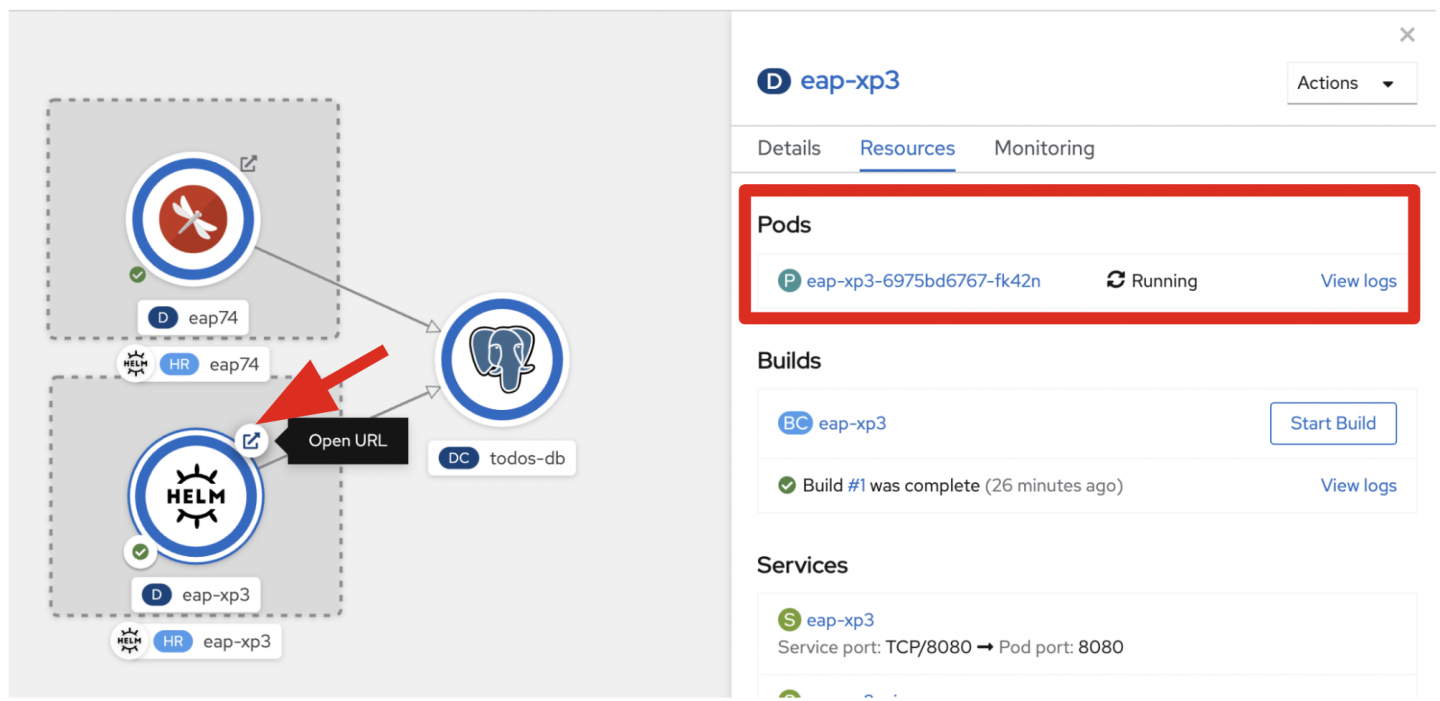
When you click on Open URL, a new web page opens automatically. Copy the route URL for the next step.
Testing the enterprise Java application
When the deployment is complete, visit your Todo front-end application by opening a new window in a web browser and pasting in the route URL you copied in the previous step. Then click on the go button shown in Figure 6.

Now you should be able to add, update, and remove items in the to-do list, as shown in Figure 7.

What’s next
This tutorial has shown how to make a bootable JAR with enterprise capabilities (e.g., database transactions) and deploy it to the cloud on Red Hat OpenShift using the JBoss EAP XP Helm chart. You can also define custom runtime environments such as health checks (e.g., livenessProbe, readinessProbe) and TLS termination. Then you can upgrade and roll back an existing Helm chart, applying the changes to the running bootable application instantly.
Additional resources:
Last updated: September 20, 2023