This article from last year details the steps and actions required to build and run your Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) image.
The purpose of this article is to describe the options needed for the RHEL WSL distribution so that it can be used as a Podman machine.
Requirements
To use the RHEL WSL image as a Podman machine, ensure that the following packages are installed:
podmanpodman-dockerprocps-ngopenssh-servernet-toolsiproutedhcp-clientsudosystemd-networkd
Luckily, all but the last package are available from the preconfigured RHEL 9 repositories. The last package (systemd-networkd) is available from the EPEL 9 repository and will need to be configured when building the image.
Build the image
Navigate to image builder (Figure 1).
On the upper right menu, enable the Preview mode (Figure 2).
Click Add blueprint to open the Create image dialog wizard (Figure 3).
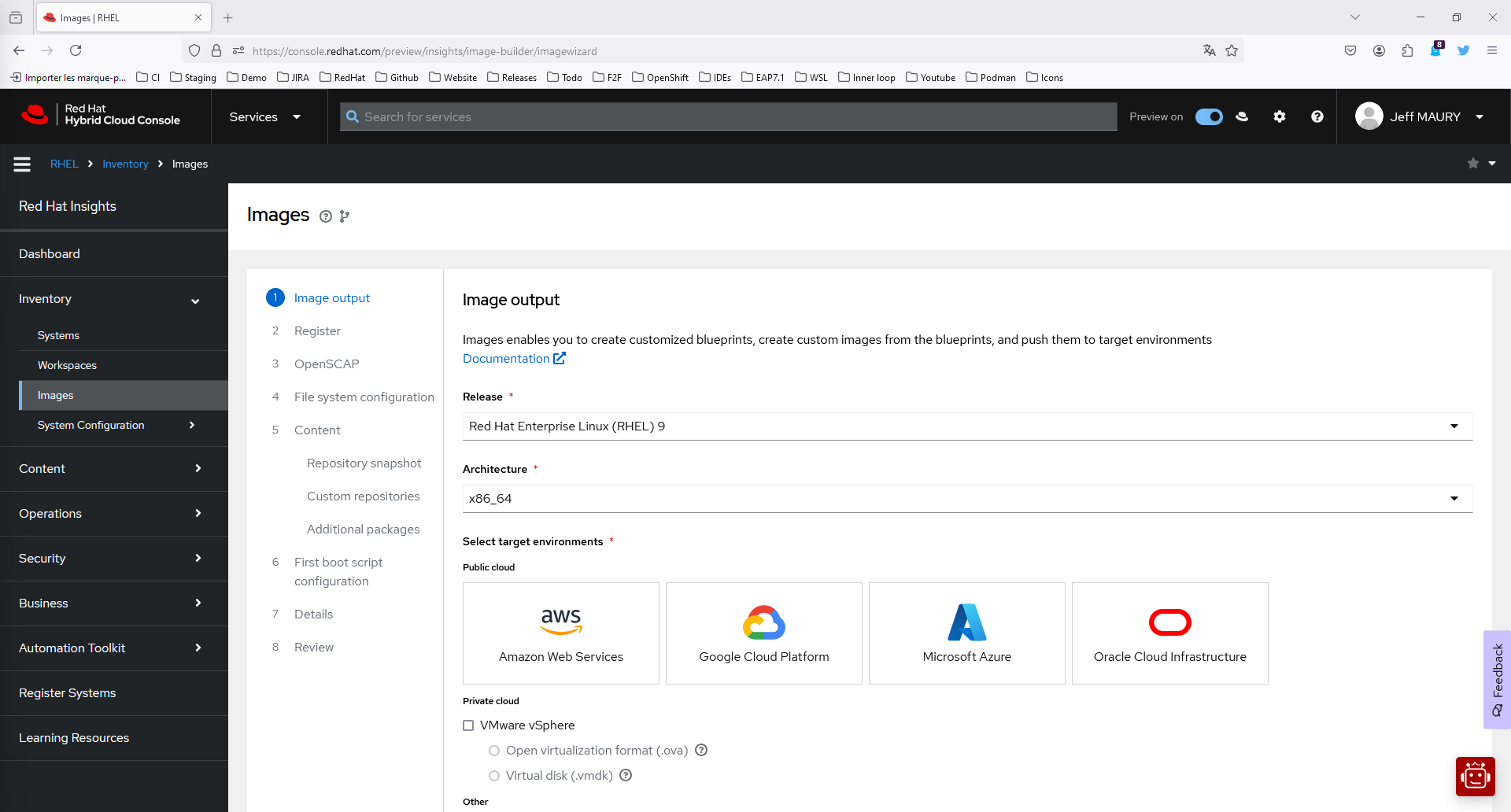
On the Image output page, select the following:
- From the Release list, select Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 9.
- From the Select target environments option, select WSL - Windows Subsystem for Linux (`.tar.gz`).
- Click Next.
On the Register page, select Automatically register and enable advanced capabilities.
- From the dropdown menu, choose an activation key to use for the image. See Creating an activation key.
- Click Next.
On the OpenSCAP page, as it is not supported for WSL images, click Next.
On the File system configuration page, select Recommended: Use automatic partitioning.
- Click Next.
On the Content page, complete the following steps to add additional packages to your image:
- On the Repository snapshot step:
- Select Use latest content.
- Click Next.
On the Custom repositories step, shown in Figure 4, click the Create and manage repositories here link.
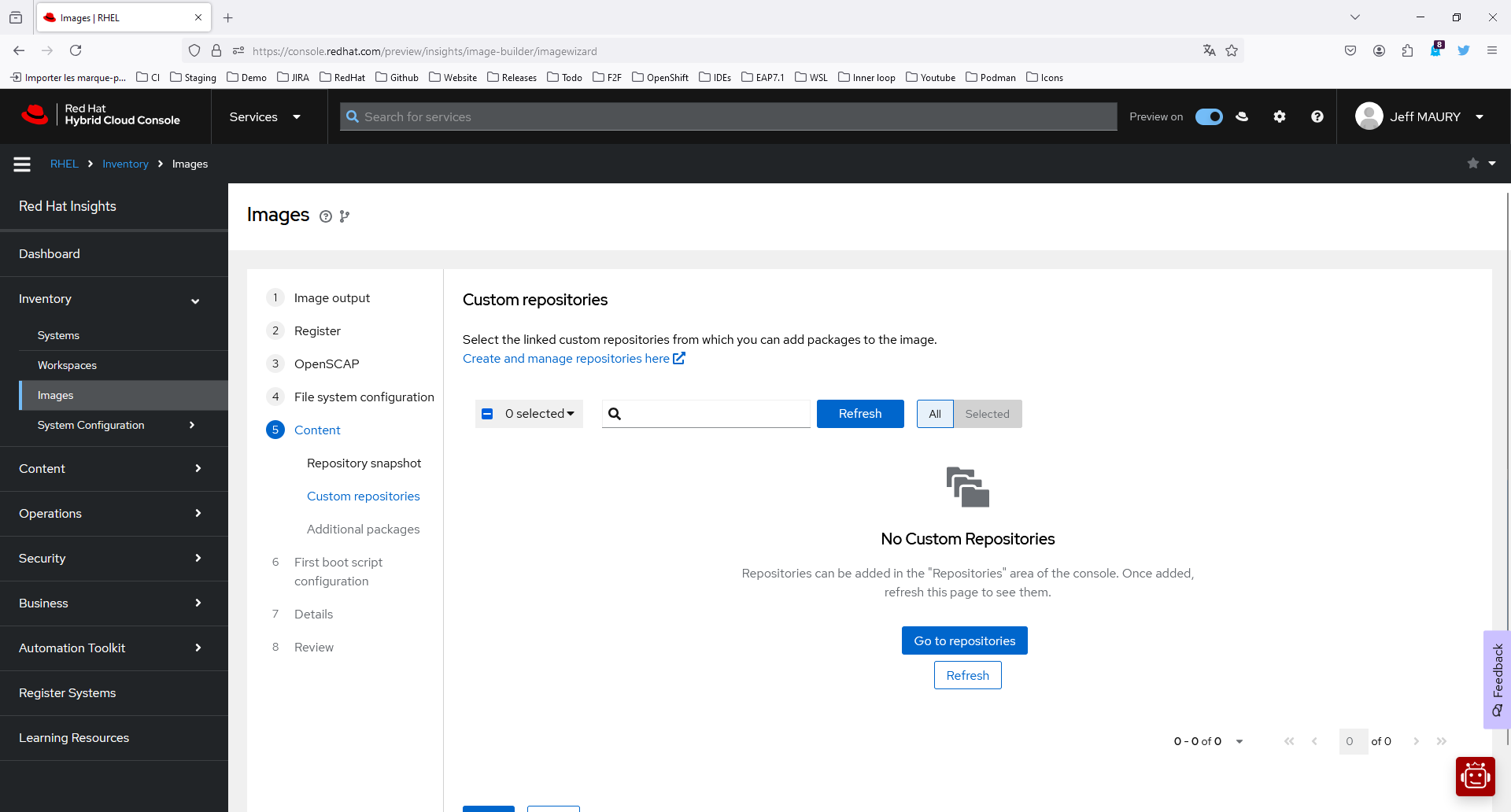
Figure 4: New image custom repositories page. This will open a new tab (Figure 5).
Figure 5: Repositories management welcome page.
Click Add repositories now (Figure 6).
Click Add repositories (Figure 7).
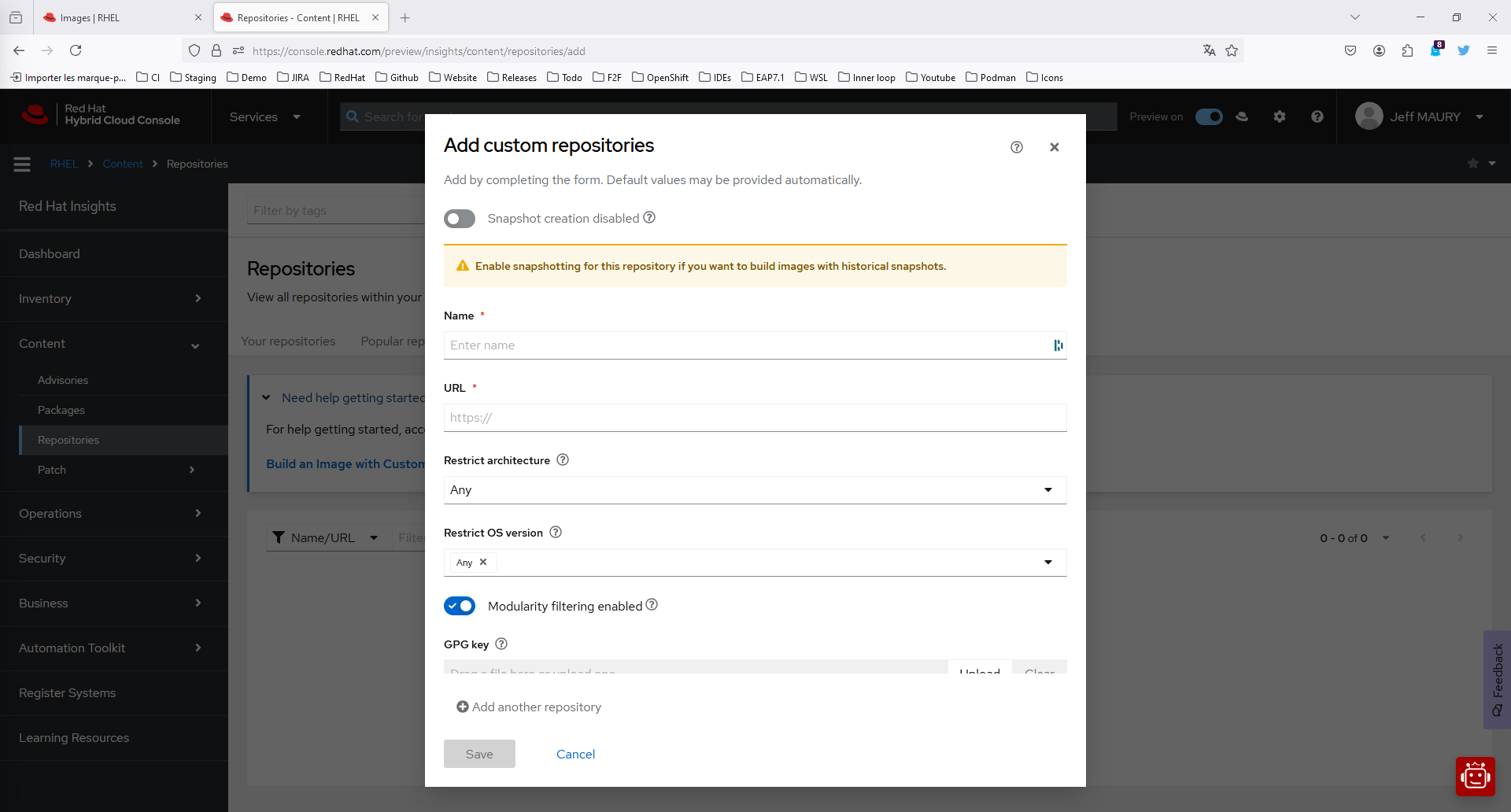
On the Add custom repositories page, select the following:
- In the Name list, enter EPEL 9.
- In the URL field, enter:
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/9/Everything/x86_64/ - In the GPG key field, enter:
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-9 - Click Save.
Close the tab and switch back to the previous one.
- In the filter input field, type
EPEL. - Select the EPEL 9 repository as shown in Figure 8.
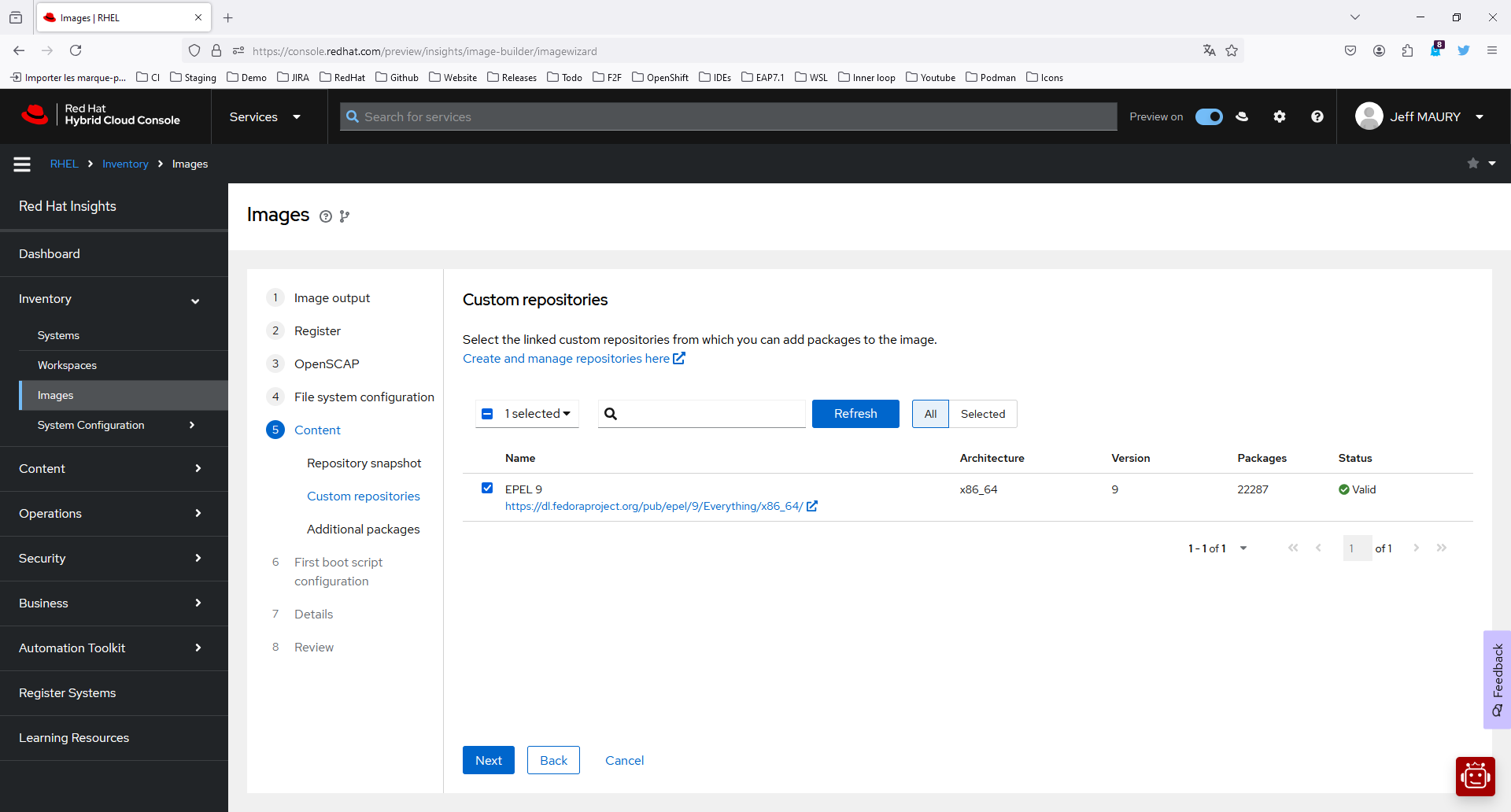
Click Next.
- On the Additional packages step:
- On the Available packages search field, enter
podmanand click the → button. - Select the
podmanandpodman-dockerpackages. - On the Available packages search field, enter
procps-ngand click the → button. - Select the
procps-ngpackage. - On the Available packages search field, enter
openssh-serverand click the → button. - Select the
openssh-serverpackage. - On the Available packages search field, enter
net-toolsand click the → button. - Select the
net-toolspackage. - On the Available packages search field, enter
iprouteand click the → button. - Select the
iproutepackage. - On the Available packages search field, enter
dhcp-clientand click the → button. - Select the
dhcp-clientpackage. - On the Available packages search field, enter
sudoand click the → button. - Select the
sudopackage and click the > button to add the selected package shown in the package search results to the Chosen packages dual list box. - On the Available packages search field, enter
systemdand click the → button. - Select the
systemd-networkdpackage. - Click Next.
- On the Available packages search field, enter
On the First boot script configuration page, click Next.
On the Details page:
- In the Blueprint name, enter
rhel-wsl. - Click Next.
On the Review page:
- Click Create blueprint and build image (Figure 9).
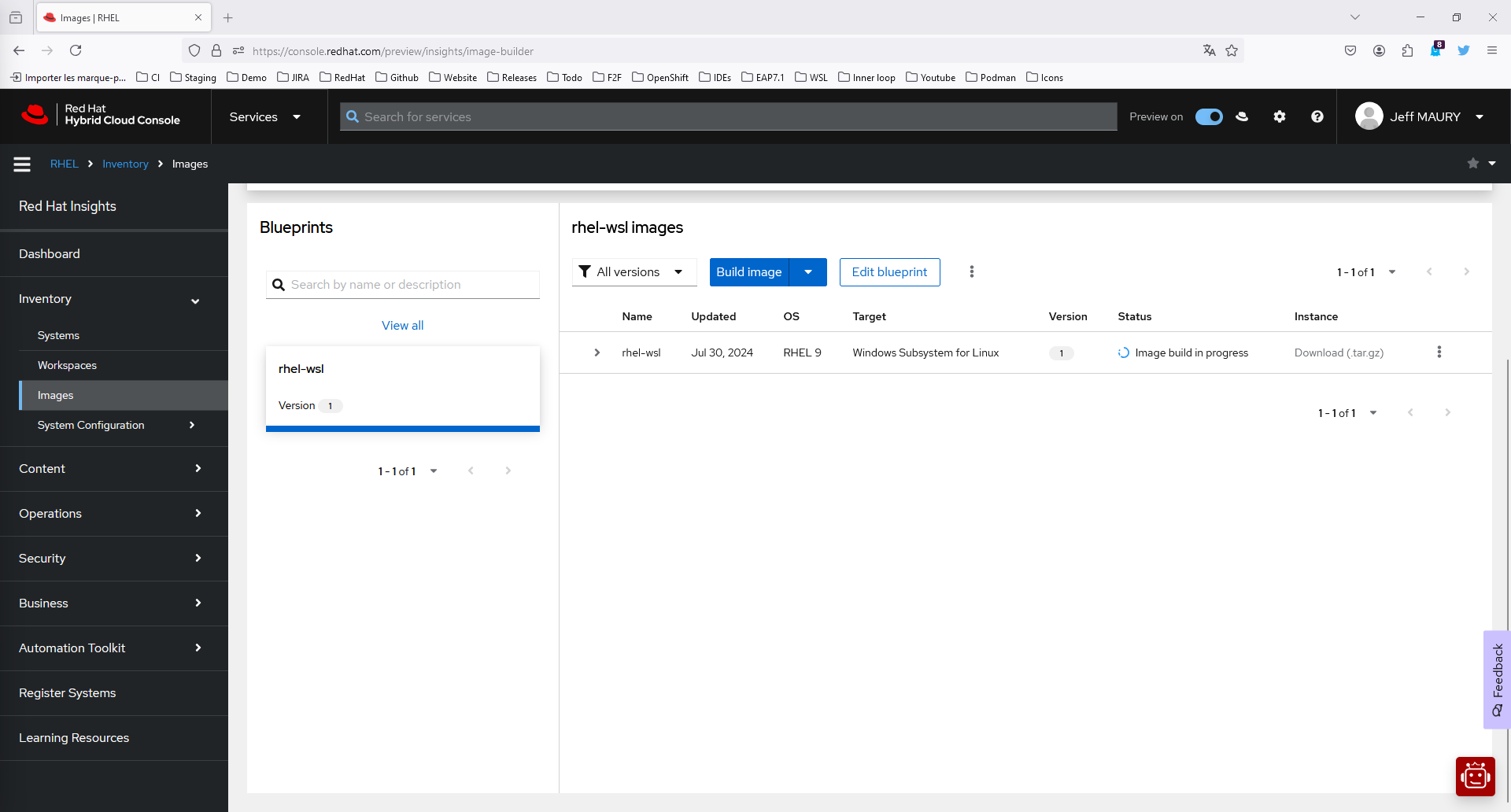
The image is being built. Once the build is finished, the download link will be available. Click the Download (.tar.gz) link and save the downloaded file to one of your local folders.
Create the RHEL WSL Podman machine
Launch Podman Desktop and go to the Settings → Resources page, as shown in Figure 10.
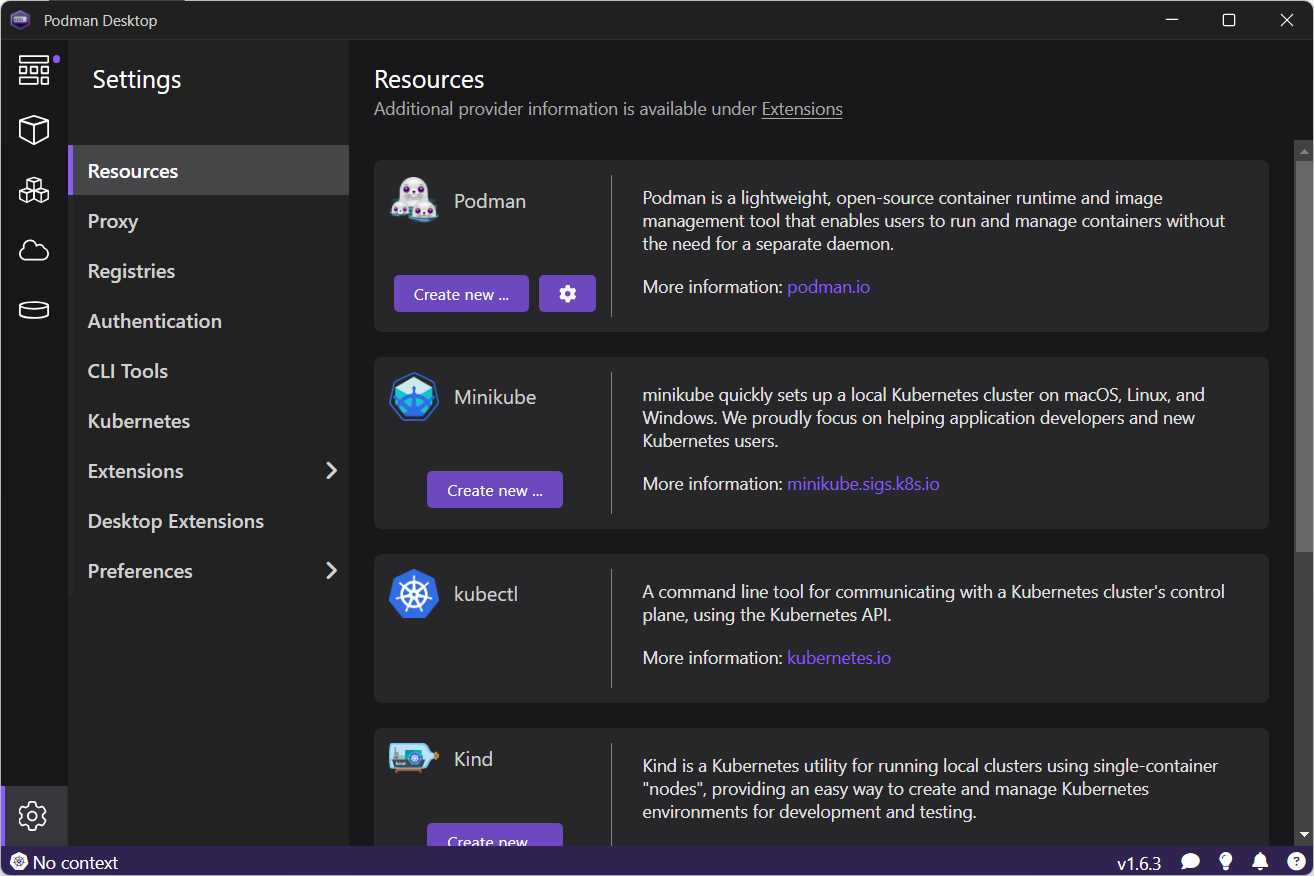
On the Podman provider, click Create new ...
On the Create Podman machine page, click the Browse button for the Image Path field and select the file downloaded from image builder. See Figure 11.
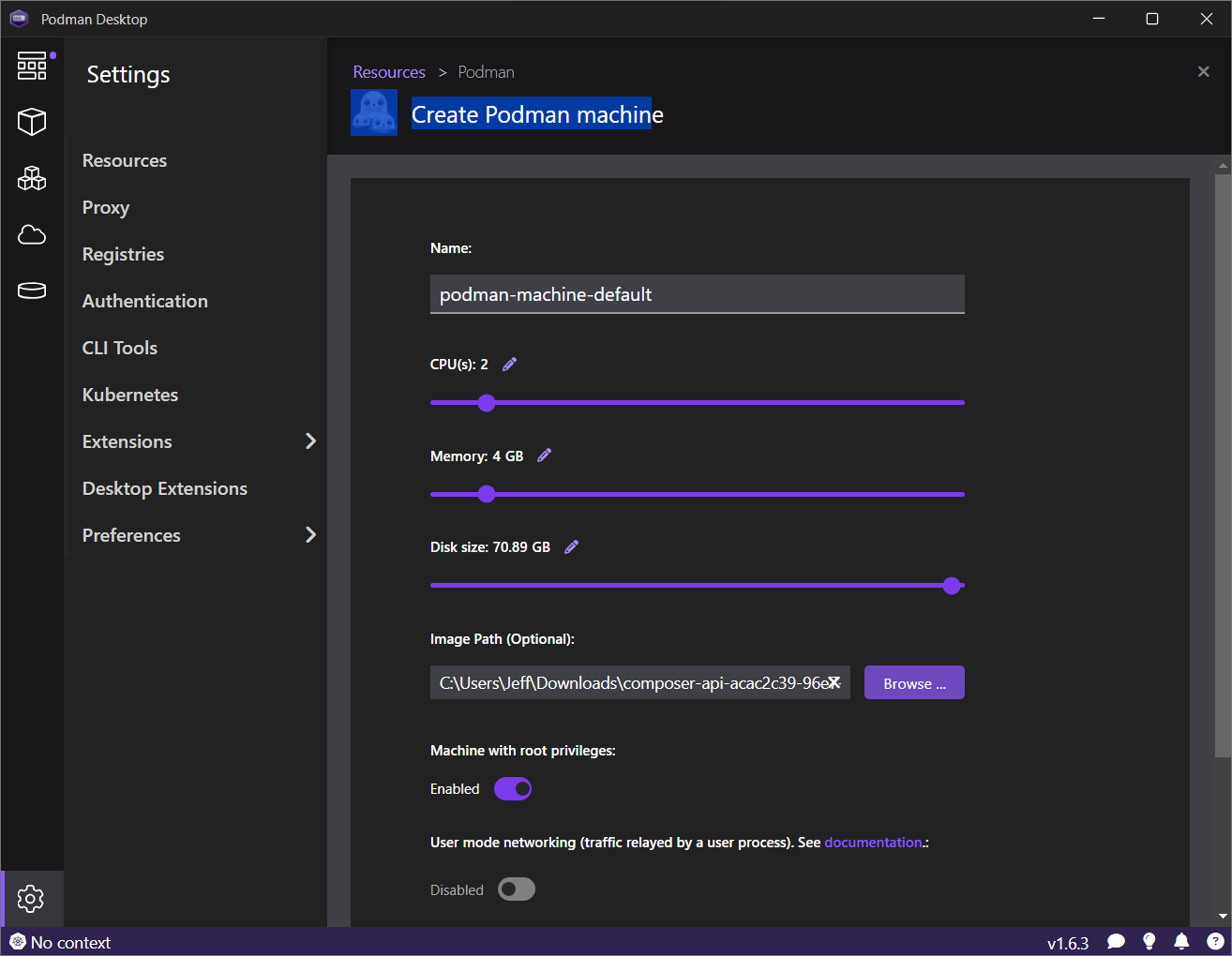
Click the Create button. The machine will be created and started. After a short time, the operation status should be reported, as depicted in Figure 12.
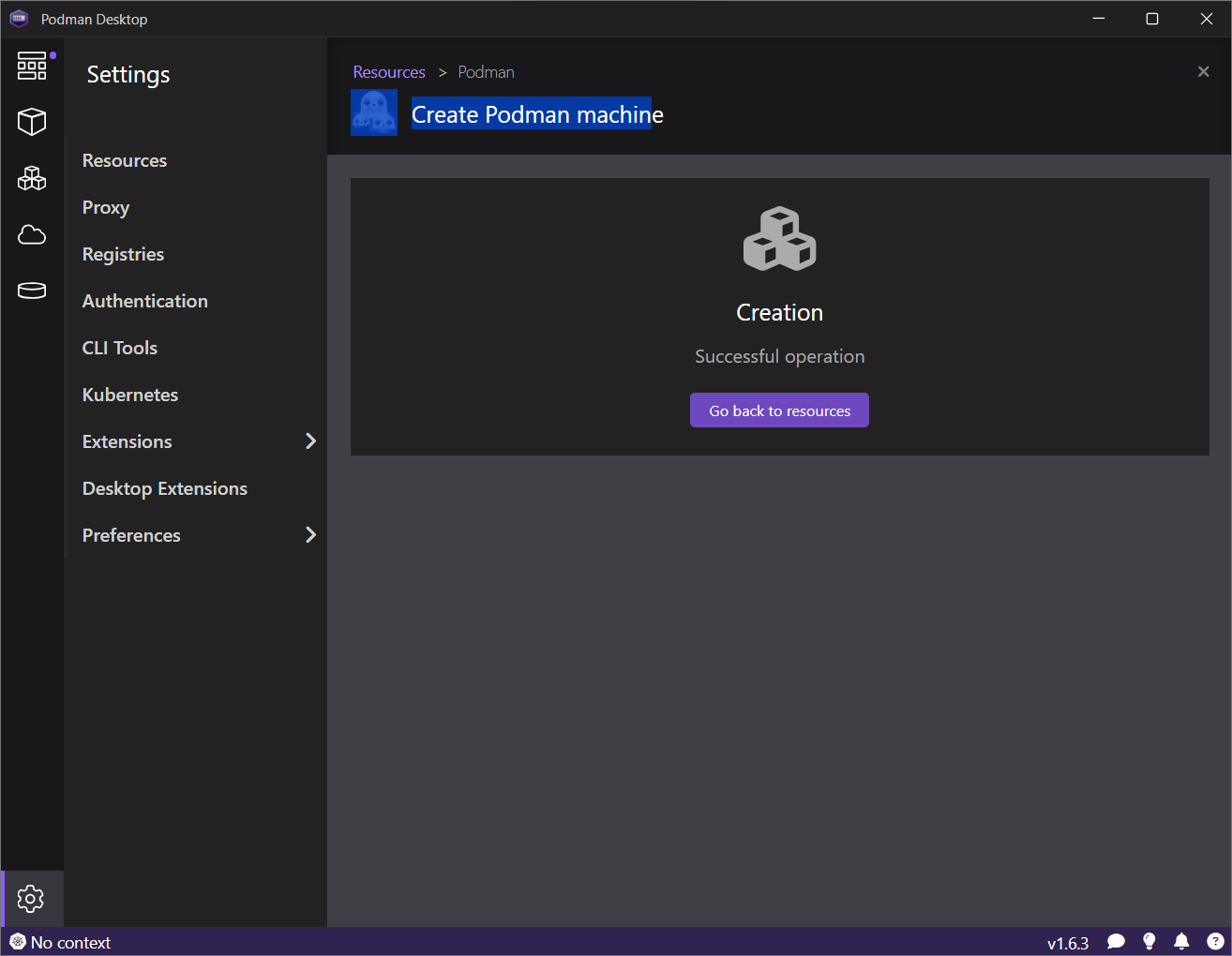
Let's play with the RHEL WSL Podman machine
Go to the Images page and pull the httpd image (Figure 13).
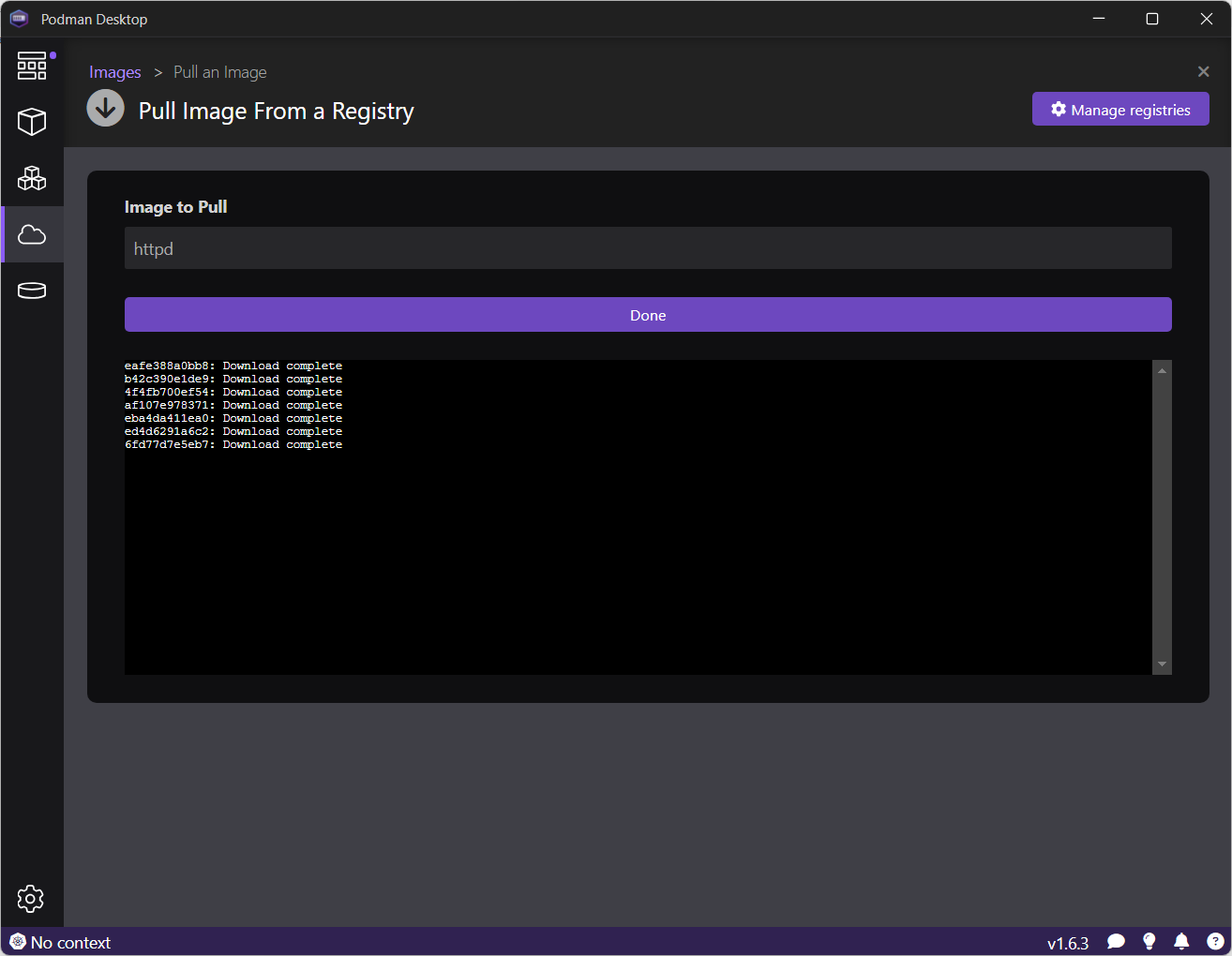
Click Done (Figure 14).
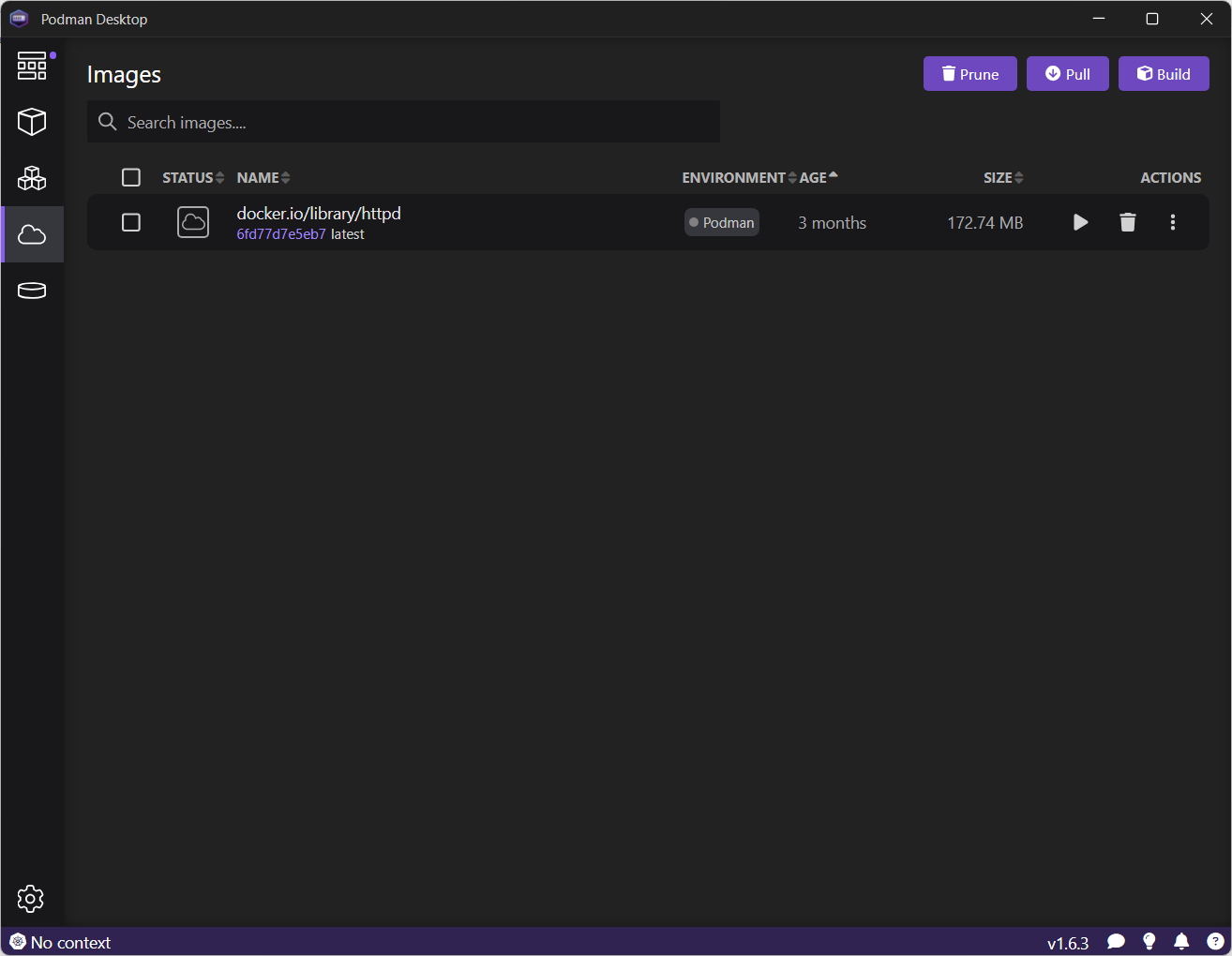
Start the image by clicking on the Run image icon (Figure 15).
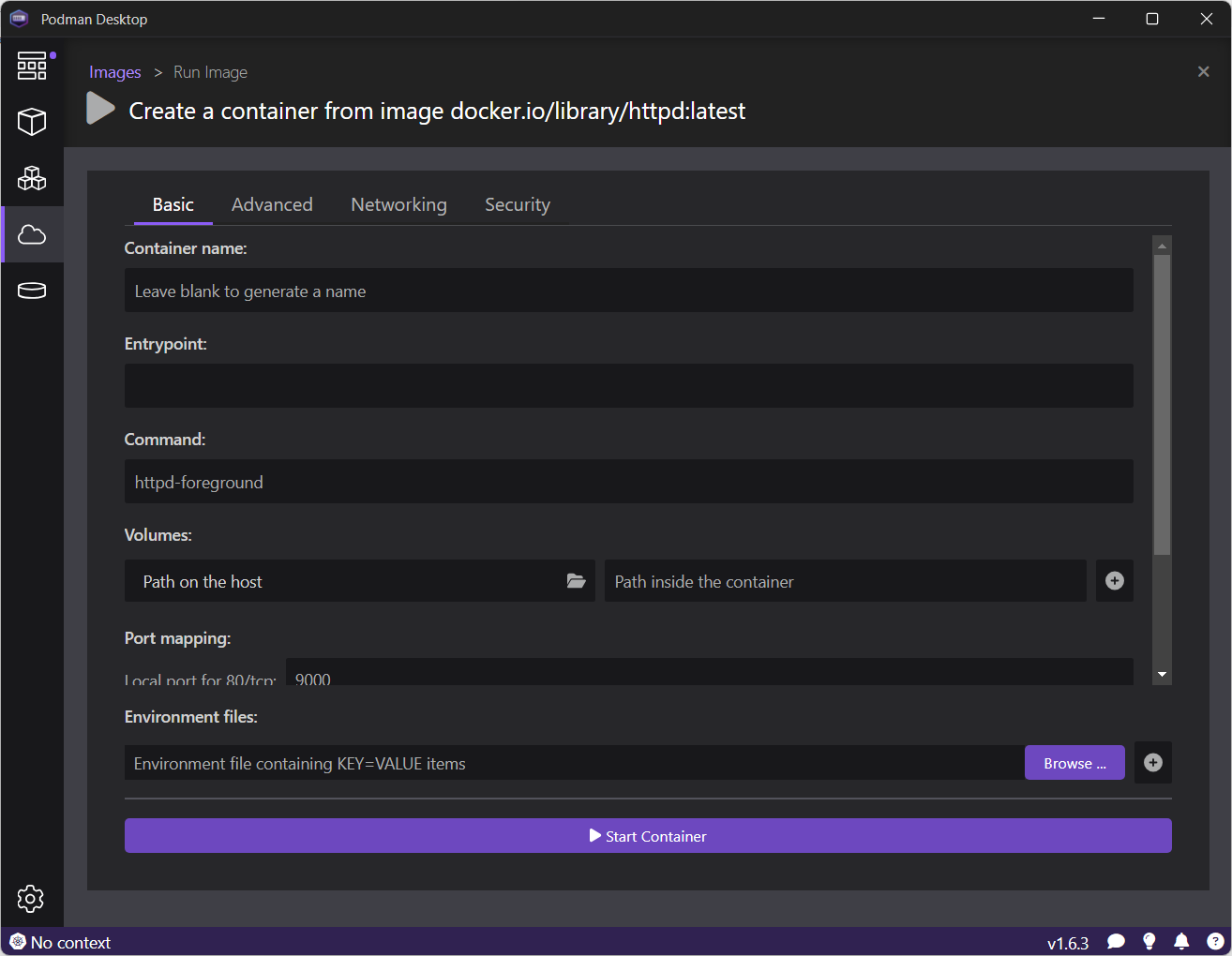
Once the container is started, you can access the Apache server on http://localhost:9000.
